
by admin | Dec 10, 2013 | Health Care Reform, Health Exchanges, Individual Exchanges, individual health insurance, SHOP Exchanges, State Exchanges

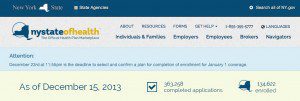
NYS Health Exchange 100,000 Enrolled. According to a USA Today article More than 100,000 enroll in N.Y. health exchange, up a third in less than two weeks according to the state Health Department .
According to the NYS Exchange site www.nystateofhealth.ny.gov– As of today, 100,881 state residents had enrolled in a health insurance plan through the state’s exchange. Additionally, 314,146 people had “completed applications” for coverage. The state did not break down the latest data based on the number of people enrolling in private insurance versus Medicaid. The state’s already “vast” Medicaid system “has been credited with having an easier transition to the health exchange.” New York state plans to enroll a total of 1.1 million people by the end of 2016
New York already has a vast Medicaid program, at an annual cost of $50 billion, it has been credited with having an easier transition to the health exchange. Reuters reported Dec. 4 that about 29,000 people signed up for health insurance through the federal HealthCare.gov website on Dec. 1 and Dec. 2 – eclipsing the 26,000 for all of October.
According to sources and our experience half of the Exchange applicants were to determined not be Medicaid eligible. The article Federal exchange sends unqualified people to Medicaid points out that some qualified Medicaid may not in fact be eligible. “The federal health care exchange is incorrectly determining that some people are eligible for Medicaid when they clearly are not, leaving them with little chance to get the subsidized insurance they are entitled to as the Dec. 23 deadline for enrollment approaches.”
New York State, unlike 36 states, runs its own exchange. The NYS website has had less issues than the troubled Federal health Exchange www.healthcare.gov. Our blog NYS Approves Health Insurance Exchange Rates describes how the new rates lower individual insurance market by 50%.
New York has various tiers of health insurers, and customers can pick from 16 insurers and 10 dental insurers. Quotes can also be viewed on our site. The program also has a small-business marketplace that offers health insurance to businesses with 50 or fewer employees. Large businesses that do not offer employees health insurance could be hit with a fine in 2015.
The exchange also offers tax credits to those who earn less than $45,960 as an individual or $94,200 as a family of four.People without health insurance would be hit with a fine on their income taxes for 2014, starting at about $95 or 1 percent of gross income. The fine can grow to as much as $695 a year , then double in 2015 and grow over time.
For more information regarding both Exchanges – Individual Exchanges or SHOP please contact our team at Millennium Medical Solutions Corp. We have Spanish, Russian, and Hebrew speakers available. Quotes can also be viewed on our site.
Governor’s Press Release
NYS Approved 2014 Exchange Rates
The following companies had health insurance plan rates for the health benefits exchange approved today by DFS. The rates approved today are subject to final certification of the insurers’ participation in the exchange.
- Affinity Health Plan, Inc.
- American Progressive Life & Health Insurance Company of New York
- Capital District Physicians Health Plan, Inc.
- Health Insurance Plan of Greater New York
- Empire BlueCross BlueShield
- Excellus
- Fidelis Care
- Health Republic
- Healthfirst New York
- HealthNow New York, Inc.
- Independent Health
- MetroPlus Health Plan
- MVP Health Plan, Inc.
- North Shore LIJ
- Oscar Health Insurance Co.
- United Healthcare
Resource:

- Click Above
Federal government health care site: www.healthcare.gov
Kaiser Health Reform Subsidy Calculator:http://healthreform.kff.org/subsidycalculator.aspx
Error: Contact form not found.

by admin | Jul 18, 2013 | Health Care Reform, Health Care Refrom, Health Exchanges, Individual Exchanges, NY News, PPACA, SHOP Exchanges, State Exchanges

NYS Approves Health Insurance Exchange Rates.
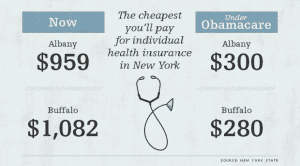
Governor Cuomo announced yesterday that New York’s Health Benefits Exchange have been approved . Additionally, the New York Times yesterday published an article highlighting that the rates in the individual market that will be offered in 2014 are at least 50 percent lower than they are now. The article link and Governor’s office press release are included below.
5 things we now know about the NYS Exchanges:
- Importantly, Insurers must still confirm that they will be in either the individual exchange and/ or shop exchange
- The rates approved yesterday are subject to final certification of the insurers’ participation in the exchange.
- Many of the networks used on the Exchange appear to be smaller than the group rated.
- Some new insurers have eneter the marketplace such as OSCAR and Freelancers. While a few such as EmblemHealth have taken a wait and see approach.
- Additionally, NYS individual market rate will drop significantly in 2014 but they have been historically always the highest. An individual/Direct Pay HMO is approximately $1,000-$1,200/month. They are still approximately 18% highest.
The Department of Financial Services (DFS) has approved New York’s Health Health Insurance Exchange rates for 17 insurers seeking to offer coverage including eight new entrants into the market that do not currently offer commercial health insurance plans. Please click the following links for the Governor’s Press Release and the Individual and Small Group rates.
Governor’s Press Release
NYS Approved 2014 Exchange Rates
The following companies had health insurance plan rates for the health benefits exchange approved today by DFS. The rates approved today are subject to final certification of the insurers’ participation in the exchange.
- Aetna
- Affinity Health Plan, Inc.

The cheapest you’ll pay for individual health insurance in NY
- American Progressive Life & Health Insurance Company of New York
- Capital District Physicians Health Plan, Inc.
- Health Insurance Plan of Greater New York
- Empire BlueCross BlueShield
- Excellus
- Fidelis Care
- Freelancers Co-Op
- Healthfirst New York
- HealthNow New York, Inc.
- Independent Health
- MetroPlus Health Plan
- MVP Health Plan, Inc.
- North Shore LIJ
- Oscar Health Insurance Co.
- United Healthcare
If you have additional questions regarding how SHOP Exchanges and Individual Exchanges can benefit you please contact our team at Millennium Medical Solutions Corp. Stay tuned for updates as more information gets released. We’re inside of 75 days until exchanges open, and information will be coming quickly in the next few months. Sign up for latest news updates.
Resource:

Click Above
Federal government health care site: www.healthcare.gov
Kaiser Health Reform Subsidy Calculator:http://healthreform.kff.org/subsidycalculator.aspx
Error: Contact form not found.
by admin | Jul 2, 2013 | Health Care Reform, Health Exchanges, individual health insurance, MEDICARE, Obamacare, State Exchanges
Obamacare 1.0: Rolling Brown Outs?
The sheer technological volume of it all could bring “rolling brown outs” similar to electrical grids. Try to imagine a scenario of credit union Experien working with IRS then Social Security & Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services’s dated mainframe computer system while balancing HIPAA and privacy sensitive information. All this while millions of people converge simultaneously onto the information highway. Visualize all of the U.S. Daily Commuters driving into Manhattan today. As reported below by Reuters’ Sharon Begley Obamacare 1.0: States brace for Web barrage when reform goes live: “Obamacare, formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA), could fail for many reasons, including participation by too few of the uninsured and a shortage of doctors to treat those who do sign up. But because its core is government-run marketplaces selling health insurance online, the likeliest reason for failure at the opening bell is information technology snafus, say experts who are helping with the rollout.” By Sharon Begley
NEW YORK | Sun Jun 30, 2013 7:03am EDT
(Reuters) – About 550,000 people in Oregon do not have health insurance, and Aaron Karjala is confident the state’s new online insurance exchange will be able to accommodate them when enrollment under President Barack Obama’s healthcare reform begins on October 1.
What Karjala, the chief information officer at “Cover Oregon,” does worry about, however, is what will happen if the entire population of Oregon – 3.9 million – logs on that day “just to check it out,” he said. Or if millions of curious souls elsewhere, wondering if Oregon’s insurance offerings are better than their states’, log on, causing Cover Oregon to crash in a blur of spinning hourglasses and color wheels and an epidemic of frozen screens.
Multiply that by another 49 states and the District of Columbia, all of which will open health insurance exchanges under “Obamacare” that same day, and you get some idea of what could go publicly and disastrously wrong.
Obamacare, formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA), could fail for many reasons, including participation by too few of the uninsured and a shortage of doctors to treat those who do sign up. But because its core is government-run marketplaces selling health insurance online, the likeliest reason for failure at the opening bell is information technology snafus, say experts who are helping with the rollout.
Although IT is the single most expensive ingredient of the exchanges, with eight-figure contracts to build them, experts expect bugs, errors and crashes. In April, Obama himself predicted “glitches and bumps” when the exchanges open for business.
“This is a 1.0 implementation,” said Dan Maynard, chief executive of Connecture, a software developer that is providing the shopping and enrollment functions for several states’ insurance exchanges. “From an IT perspective, 1.0’s come out with a lot of defects. Everyone is waiting for something to go wrong.”
Two states that intended to build their own exchanges, Idaho and New Mexico, announced this spring that because of the tight timeline and daunting challenges they would have the federal government operate their IT systems.
“Nothing like this in IT has ever been done to this complexity or scale, and with a timeline that put it behind schedule almost before the ink was dry,” said Rick Howard, research director at the technology advisory firm Gartner.
WHAT COLOR WAS YOUR VOLVO?
The potential for problems will begin as soon as would-be buyers log onto their state exchange. They’ll enter their name, birth date, address and other identifying information. Then comes the first IT handoff: Is this person who she says she is?
To check that, credit bureau Experian will check the answers against its voluminous external databases, which include information from utility companies and banks on people’s spending and other history, and generate questions. The customer will be asked which of several addresses he previously lived at, for example, whether his car has one of several proffered license plate numbers, and what color his old Volvo was.
It’s similar to the system that verifies identity for accessing personal Social Security information. If someone gets a question wrong, he will be referred to Experian’s help desk, and if that fails may be asked to submit documentation to prove he is who he claims to be.
The next step is determining if the customer is eligible for federal subsidies to pay for insurance. She is if she is a citizen and her income, which she will enter, is less than four times the federal poverty level. To verify this, the exchange pings the “federal data services hub,” which is being built by Quality Software Services Inc under a $58 million contract with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS).
The query arrives at the hub, which does not actually store information, and is routed to online servers at the Internal Revenue Service for income verification and at the Department of Homeland Security for a citizenship check.
The answers must be returned in real time, before the would-be buyer loses patience and logs off. If the reported income doesn’t match the IRS’s records, the applicant may have to submit pay stubs.
These federal computer systems have never been connected before, so it’s anyone’s guess how well they’ll communicate.
“The challenge for states,” said Jinnifer Wattum, director of Eligibility and Exchange Solutions at Xerox’s government healthcare unit, is that they have to build “the interfaces needed with the federal data services hub without knowing what this system will look like.” That makes the task akin to making a key for a lock that doesn’t exist yet.
CMS’s contractors are working to finish the hub, but “much remains to be accomplished within a relatively short amount of time,” concluded a report from the Government Accountability Office (GAO), the investigative arm of Congress, in June. CMS spokesman Brian Cook said the hub would be ready by September, and that the beta version had been tested for its ability to interact with the exchanges Oregon and Maryland are building.
The federal hub has to verify even more arcane data, such as whether the insurance offered to a buyer through his job is unaffordable, in which case he may qualify for federal subsidies, and whether the buyer is in prison, in which case she is exempt from the mandate to purchase insurance.
If someone’s income qualifies him for Medicaid, or his children for the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), software has to divert him from the ACA exchange and into those systems. Many of the computers handling Medicaid and CHIP enrollment are, as IT people diplomatically put it, “legacy systems,” meaning old, even decades old.
Many are mainframes, lacking the connectivity of cloud computing. They typically process eligibility requests in days, not seconds.
The legacy systems “rely on daily or weekly batch files to pass information back and forth,” and often require follow-up phone calls, said Wattum of Xerox, which is working to configure Nevada’s exchange so it can interface with the federal hub.
‘NO WRONG DOOR’
A “we’ll call you” message is unacceptable under Obamacare, which has a “no wrong door” goal: A buyer must never come to a dead end. If she is diverted to Medicaid, for instance, she must not be required to resubmit information, let alone wait a week for an answer about whether she’s now enrolled.
State IT systems must therefore “be interoperable and integrated with an exchange, Medicaid, and CHIP to allow consumers to easily switch from private insurance to Medicaid and CHIP,” said an April report from the Government Accountability Office (GAO), the investigative arm of Congress.
To make all those systems communicate, the state exchanges must either develop entirely new systems or use application programming interfaces (APIs) that work with the legacy systems to exchange data in real time. APIs are programming instructions for accessing Web-based software applications.
GAO’s Stan Czerwinski compares the necessary connectivity to adapters that let Americanelectronics work with European outlets.
State officials told the GAO that verifying eligibility, enrolling buyers and interfacing with legacy systems are the most “onerous” aspects of developing their exchanges, “given the age and limited functionality of current state systems.”
A key goal for exchange officials is keeping would-be buyers in the portal so they don’t give up and use a state’s ACA call center, which could quickly be swamped.
To avoid this, Oregon brought in potential users to test design prototypes, recorded what people did and where they had trouble, and tweaked the consumer interface to make it as user-friendly as possible, said Karjala.
“Even with that, if you have a family of four and you’re eligible for a tax credit to offset your premium,” he said, “you could be sitting at the computer for a long time.”
What everyone hopes to avoid is a repeat of the early days of the Medicare prescription-drug program in 2006. Some seniors who tried to sign up for a plan were mistakenly enrolled in several, while others had the wrong premium amounts deducted from their Social Security checks.
Another challenge is capacity. Websites regularly crash when too many people try to access them.
“I had no choice but to be extremely conservative” in estimates of how many simultaneous users Cover Oregon has to be prepared for, Karjala said. “Building capacity is the only way to avoid the spinning hourglass or the site freezing, so in our performance testing we’re seeing what happens if the whole U.S. population came to Cover Oregon to check it out.”
This summer, state exchanges will test their ability to communicate with the federal data hub, whose security frameworks and connectivity protocols are still works in progress. But whether Obamacare 1.0 flies won’t be known until the new health plans take effect on January 1. Robert Laszewski, president of Health Policy and Strategy Associates Inc, a consulting firm, said he wouldn’t be surprised if some patients showing up at doctors’ offices next year with Obamacare policies are told their insurers never heard of them.
(Additional reporting by Caroline Humer; Editing by Michele Gershberg and Prudence Crowther)
by admin | Mar 7, 2013 | Health Care Reform, Health Exchanges, State Exchanges
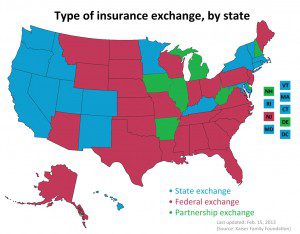
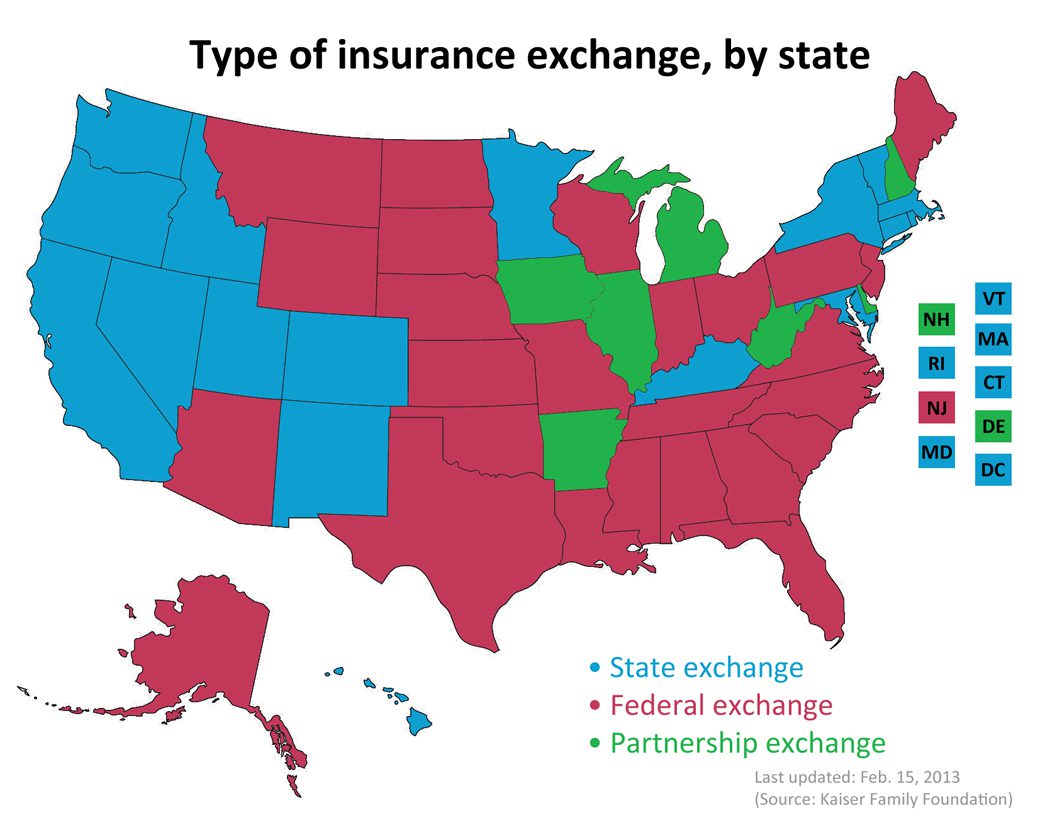
Map of State Exchanges Final. The final map of 2014 State Exchanges or health insurance marketplaces are now in.
States have had the option of either using Federal Grants to establish their own Exchanges or letting the Federal run their State’s Exchange. There is even a middle version, a Partnership Exchange Program. Under this arrangement, the State might oversee the selection and management of health plans and assisting people with enrollment. The federal government would have primary responsibility for the remaining marketplace operations, including managing the marketplace, their websites and call centers, accepting applications, and determining eligibility for premium subsidies.
Seventeen states and the District of Columbia have received conditional approval from HHS to operate a state-run marketplace in 2014. These states are: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Hawaii, Idaho, Kentucky, Maryland, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Nevada, New Mexico, New York, Oregon, Rhode Island, Utah, Vermont, and Washington.
This map is very close to last years blog we posted Map of State Exchanges Status May 2012 . For the most part this goes by partisan lines with majority of Federally Run State Exchanges located in GOP Governor States. An example of this is highlighted in our blog on NJ Exchange Chrstie Rejects State Exchange.
It is vital that as many uninsured’s get health coverage. Nationally approximately 30 million people are expected to gain coverage with 600,000 in States like NY.
Error: Contact form not found.

by admin | Mar 4, 2013 | Health Care Reform, Health Exchanges, Individual Exchanges, PPACA, SHOP Exchanges, Small Business Group Health, State Exchanges, Tax

Pay or Pay Employer Guide
Pay or Play Employer Guide
Tick! tick! tick! As the 2014 Employer Mandate to either pay or play gets closer the nation’s employers move a step closer to having to make a decision: Do I play or pay? This Employer mandate under Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) does not apply to smaller groups under 50 FTE (full time equivalent) employees. Many small groups such as food service industry, retailers, construction etc. in fact have many FTE and while they may work minimal hours can trigger the “pay or play” mandate.
The IRS has released recently guidance published in the form of a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM), addresses a number of issues tightly linked to an array of practical considerations related to the employer mandate. These include defining a “large employer,” determining “full-time” status for employees, clarifying the meaning of “dependents,” and determining what constitutes “affordable” coverage.
The guidance also tackles several stickier questions such as how and whether to count foreign or seasonal workers, as well as how to calculate the full-time status of employees who work unusual hours, such as teachers or airline pilots.
Three safe harbors relating to the provision of “affordable” coverage to employees in order to avoid exposure to the mandate penalties are also included in the guidance. Transition relief is offered in recognition of certain employers’ needing time to bring their plans into compliance.
Still, there are several regs that the IRS is awaiting commentary and resolution on due on March 18, 2013.
A Q&A summary of the rule has been released by the IRS and is available by clicking here.
Some employers assert that the play-or-pay mandate will raise their costs and force them to make workforce cutbacks. As a result, a number are considering eliminating their health care coverage altogether and instead paying the penalty on their full-time employees. While the “pay” option might be worth considering, there are strong reasons why employers should look carefully at all of their options and do their best to calculate the actual outcomes of each.
Other Key Issues Addressed in the Proposed Rules
Additional issues addressed in the proposed regulations include:
- Determining which employers are subject to the “pay or play” requirements;
- Determining who is a full-time employee, including approaches that can be used for employees who work variable hour schedules, seasonal employees, and teachers who have time off between school years;
- Determining whether coverage is affordable and provides minimum value; and
- Calculating the amount of the penalty due and how the penalty will be assessed.
When conducting a cost-benefit analysis, the key tax issues the employer should consider are:
- Employer Tax Penalty for Not Offering “Qualified” Group Health
- Not applicable for employers with less than 50 FTEs
- $2,000 penalty per full-time employee (minus 30 employee credit)****
- Employer Tax Penalty for Offering “Qualified” Health That is Not “Affordable”
- Not applicable for employers with less than 50 FTEs
- $3000 per employee receiving subsidy
Example:
Jungle Corp. has 100 full-time employees and is a leader in its market, using a talent differentiation strategy. Jungle’s family coverage costs $15,000, of which employees pay $3,000. Bob Smith, a highly skilled worker with a strong performance record, earns $50,000 and has family coverage through Jungle’s plan.
On Jan. 1, 2014, Jungle Corp. announces it is dropping its group health plan coverage and will instead pay the $2,000-per-full-time-employee penalty. On Jan. 2, Bob walks into HR and asks about receiving replacement compensation for the $12,000 that the business had been paying toward his family coverage.
Wanting to retain Bob in accordance with its strategy of maintaining market leadership with an experienced workforce, Jungle offers him another $12,000. But clever Bob points out that his share of Social Security and Medicare payroll (FICA) taxes will take a bite out of that $12,000, as will federal and state income taxes, so the HR manager agrees to make good on those amounts as well. Of course, the company will also have to pay its share of FICA taxes on Bob’s additional compensation. As a result, instead of paying $12,000 toward Bob’s family coverage using pre-tax dollars, Jungle Corp. now finds itself paying an additional:
- Bob’s salary adjustment: $14,500
- Employer’s share of FICA taxes: $1,109
- Excise tax (penalty): $2,000
———————————- - Total: $17,609
(versus $12,000 currently)
Similar per-employee costs will be reflected across the company’s workforce. A move that seemed like a no-brainer, the consequences could make you look silly.
For More Information
Due to the complexity of the law in this area, and the absence of finalized guidance, employers are strongly advised to review their benefit plans to prepare for the changes ahead. Additional information regarding the penalty is featured on our Employer Shared Responsibility page.
Ask us about our Health Care Reform Compliance Audit Assessments. See Health Care Reform Timeline and Preparing for Reform by UHC.
In the coming months, Millennium Medical Solutions Inc will host seminars and will share information you’ll need to know as the countdown continues to October 1st. Please contact us for immediate information on how to implement these initiatives for your group-specific needs at info@medicalsolutionscorp.com or Call (855) 667-4621.

by admin | Dec 11, 2012 | Health Care Reform, Health Exchanges, Obamacare, State Exchanges
Governor Christie vetoes Health Insurance Exchange – Washington Post “Christie Vetoes Obamacare”.
“New Jersey and all other states still await substantial federal guidance on the functioning of all three types of exchanges,” Mr. Christie said in his veto message. “To be sure, the decision of whether to move forward with a state-based exchange can only be fully understood when competitively compared to the overall value of the other options.”
States have until Dec. 14 to decide whether to establish a state-based exchange. They have more time to decide whether to partner with the federal government or let federal bureaucrats design and run the state exchange. Many states with Republican governors have said they would not participate in the process, citing their opposition to the law and its potential costs. This is the current Map of State Exchange Status.
What is an Exchange? One of the centerpieces of the recently passed Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) is the establishment of state based health insurance exchanges by the year 2014.
An “Exchange” is a mechanism for organizing the health insurance marketplace to help consumers and small businesses shop for coverage in a way that permits easy comparison of
available plan options based on price, benefits, service and quality. By pooling individuals and small groups together, transaction costs can be reduced and transparency can be increased.
Exchanges can create more efficient and competitive markets for individuals and small employers.
States have until Dec. 14 to decide whether to establish a state-based exchange. They have more time to decide whether to partner with the federal government or let federal bureaucrats design and run the state exchange. Many states with Republican governors have said they would not participate in the process, citing their opposition to the law and its potential costs.
Many Republican governors were saying before the Court ruling that the Medicaid expansion was yet another unfunded federal mandate they could not afford. Yes the Supreme Court ruling has given the Republican governors enormous leverage. Republican governors have long argued that state control and flexibility can save lots of Medicaid money. If they put a reasonable plan on the table to expand their Medicaid programs to 133% of poverty–one that saves at least as much as their state match–it could be a win for everyone. The Republican governors get their flexibility and the Obama administration gets their expansion.









