With only 6 month away from full implementation of 2014 Patient Protection Affordability Care Act (PPACA) employers are understandably uncertain. Below are Health Care reform – five things employers can do now to prepare and take action.
UPDATE JULY 2nd: Since blog posting the President Administration has delayed 1 year Employed Shared Responsibility Mandate i.e. Pay or Play to Jan 2015.
1. Employee Communications
Employers must notify employees of the online insurance marketplace known as a Healthcare Exchange. Recently released federal guidelines require employers to notify their workers of eligibility requirements for their state exchange starting Oct. 1, 2013 Open Enrollments for Jan 2014 effective date. To the relief of many, the U.S. Labor Department also provided model notices that employers can give to their workers, which eliminates the need to develop their own notifications.
Additionally, Employers sponsoring a health plan must give employees a Summary of Benefits and Coverage (SBC). The purpose of the Summary of Benefits and Coverage, or SBC, is to present benefits and coverage information in clear language and in a consistent format. Inspired by the Nutrition Facts Label on packaged food, the SBC (pdf) includes two medical scenarios: having a baby and managing Type II diabetes. It estimates how much a patient would pay for medical care in each scenario with specific insurance plans.
Important things to know about the SBC:
- The health insurance companies will create the SBCs.
- It’s the employer’s responsibility to distribute the SBCs to employees.
- This requirement applies to health plan renewals after Sept. 23, 2012.
- Department of Labor will NOT impose penalties for non-compliance with the SBC notice during the first year as long as employers show a “good faith” effort to comply. Read the FAQ on SBC and ACA pdf here.
- Medicalsolutionscorp.com has suggestions to help employers comply with the SBC distribution requirements
2. Determining which Employers must offer health care.
Because employers with 50 full-time equivalents face penalties for not providing affordable, minimum value insurance an employer should know whether it is subject to these requirements or not. Common law employees of the employer and any commonly controlled company must be counted. Employers with temporary or leased employees will want to discuss with their advisors whether these employees will be considered “common law employees” for purposes of determining how many FTEs an employer has. Employers with employees who are paid based on unique payment models (stipends, work product, etc) will want to discuss how to calculate these employee hours with their benefits advisors.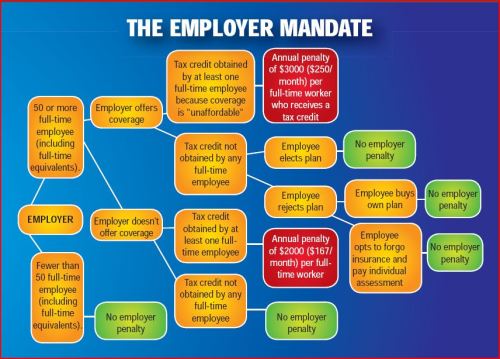
- Employers with 50 or more employees will incur penalties of up to $2,000 per employee if they cancel their existing health care program (which up until 2014 would be considered an optional benefit to provide). They will also incur penalties if their plan is too costly, and they do not meet the affordability standards.
- Employers with less than 50 employees will not incur penalties if they cancel their health care plan, and that decision will need to be made on a business by business basis. They can also choose to offer partial coverage and contribute up to the minimum 50% of single coverage not to exceed 9.5% employee
The good news is Employers can subtract 30 FT employees. This portion is known as the Employer “play or pay” option. Specific case example and details are found at Pay or Play Employer Guide.
3 Health Care Small Business Tax Credit Calculator
To encourage businesses to offer health benefits to their employees, the federal government is offering tax credits to small businesses. These credits are available to an estimated 4 million small businesses, including nonprofits.The IRS has set up a web page with information: Small Business Health Care Tax Credit for Small Employers. The maximum “credit” (which offsets taxes dollar for dollar and is better than a “deduction” which reduces taxable income) is 35 percent of the amount an employer pays towards employee health insurance.
Who’s eligible?
To qualify, small employers must:
- Have fewer than the equivalent of 25 full-time workers
- Pay average annual wages below $50,000
- Cover at least 50% of the cost of health care coverage for their workers
Because of the high wages paid in most industries in NY/NJ/CT Tri State, few small employers that provide coverage pay such a low average wage. Note, however, that the calculation of average wages and number of employees excludes the wages of an owner and his or her family members.
medicalsolutionscorp.com help clients gather the appropriate information and do a preliminary estimate of the credit amount. This information will help you and your accountant determine whether applying for the credit makes financial sense. Find out what the new tax credit could mean for your coverage. Call us at 855-667-4621.
4. Determine affordability
Beginning Jan. 1, 2014, an employer with 50 or more employees must pay a tax penalty if they either: a) Do not provide health insurance with minimum benefits or 60 percent of healthcare expenses; b) Require employees to contribute more than 9.5 percent of an employee’s household income for the health insurance and those employees obtain a government subsidy for coverage.
Companies will be required to pay $3,000 per employee without affordable coverage. (Note: there are a number of caveats that might affect the actual penalty paid, so consult your tax advisor.)
This chart shows employer penalties under the ACA, referred to as “shared responsibility.” Employers wishing to more precisely calculate their potential penalty liability should read the document we prepared, Calculating the Potential ACA Employer Tax Penalty.
5. What does Full Time Equivalent Mean?
It is crucial to Understand the difference between FT and Full Time Equivalent. To determine the FTE (Full Time Equivalent) you must count FT and PT employees. Full Time Employees are those working 30 hours+/week.* The number of full-time employees excludes those full-time seasonal employees who work for less than 120 days during the year.4 The hours worked by part-time employees (i.e., those working less than 30 hours per week) are included in the calculation of a large employer, on a monthly basis, by taking their total number of monthly hours worked divided by 120.
For example, a firm has 35 full-time employees (30+ hours). In addition, the firm has 20 part time employees who all work 24 hours per week (96 hours per month). These part-time employees’ hours would be treated as equivalent to 16 full-time employees, based on the following calculation:
20 employees x 96 hours / 120 = 1920 / 120 = 16
Thus, in this example, the firm would be considered a “large employer,” based on a total full-time equivalent count of 51—that is, 35 full-time employees plus 16 full-time equivalents based on part-time hours.
In the coming months, Millennium Medical Solutions Inc will host seminars and will share information you’ll need to know as the countdown continues to October 1st. Error: Contact form not found.
This blog is not intended to represent legal advise and one should consult with a tax and/or legal expert.
* IRC 4980H(c)(4)
Disclaimer: This blog is not intended to represent legal advise and one should consult with a tax and/or legal expert.
