
by admin | Aug 18, 2011 | group health insurance, healthcare, Hospitals

After balancing the budget and announcing $2.4 trillion in government spending cuts over ten years, politicians and media pundit are insisting that it is only the beginning of the attack on health care, pensions and other social programs.
So why is balancing the budget and cutting medicare so bad for the Privately Insured? After all, the Democrats have made sure the automatic cuts leave Medicare benefits untouched, and the Republicans have blocked any new taxes.
Everyone is content right? Or so it seems. But the truth is that cutting payments to Medicare providers will mean some Americans are going to pay more. It may not be called a tax, but if you’re covered by private health insurance, money will be coming out of your pocket nonetheless.
Here’s how cuts in Medicare affects the rest: If a hospital provides a service that costs $1,000,000, and the government elects to pay just $980,000, the $20,000 gap doesn’t disappear. The hospital has to cover it somehow. It will likely do so by shifting the costs to commercial insurers, which eventually means higher premiums. This cost shifting is nothing new-it’s been happening for years-but more cuts will just make it worse.
NY Hospitals in particular have felt Federal Funding cuts for teaching hospitals over the last decade. This has been a contributing factor to St. Vincents declaring bankruptcy last January. Many surviving hospitals however have the size to negotiate effectively with private insurers to make up that funding short fall.
So guess who makes up that difference? The fact remains, if you don’t deal with underlying costs, you’re not fixing the problem, you’re just covering it up.
by admin | May 12, 2011 | Health Care Reform, healthcare, PPACA
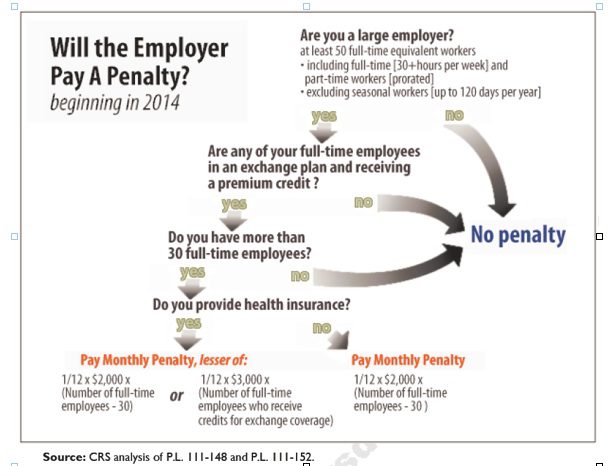
Larger employers that don’t offer minimum essential health coverage to full-time workers may face penalties under health care reform if any full-time employees receive a government premium credit or subsidy to buy their own insurance through an exchange.
The so-called employer mandate and the health insurance exchanges both go into effect in 2014 under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act.
The penalties generally apply to all employers with 50 or more full-time equivalent employees. An employer with at least 50 FTEs that provides access to coverage but fails to meet certain requirements, outlined below, may also be subject to a penalty.
To determine the FTE (Full Time Equivalent) you must count FT and PT employees. Full Time Employees are those working 30 hours+/week. See blog post “What does FTE mean?”
Affordability of the employer plan remains a consideration, however, since just one employee qualifying for federal premium assistance for exchange coverage will trigger a penalty for employers with 50 or more employees
Minimum essential coverage generally includes any coverage offered in the small or large group markets. Excepted benefits, such as limited-scope dental or vision offered under a separate policy, certificate or contract of insurance and Medicare supplemental plans, do not qualify.
Penalties explained
Starting in 2014, large employers that don’t offer coverage face a penalty of $2,000 per full-time employee (excluding the first 30) if at least one FTE receives a government subsidy to buy coverage on an exchange. This is sometimes referred to as the “play or pay” penalty.
Employers that offer coverage to employees may still face a “free rider” penalty if the coverage offered is deemed unaffordable or low in value.
If an employer offers coverage, but a full-time employee receives a premium credit subsidy through an exchange, the employer must pay an assessment equal to the lesser of:
- $3,000 for each employee that receives a subsidy
- $2,000 for each full-time employee after the first 30
The monetary penalties listed above are annual figures and may be pro-rated to the number of months for which the penalty applies.
Who’s eligible for a subsidy?
Employees who are offered coverage from their employer could be eligible for subsidies on the exchange if they don’t qualify for Medicaid or other programs, are not enrolled in their employer’s coverage and meet either of the following conditions:
- The employee’s share of the premium exceeds 9.5 percent of their household income
- The plan pays for less than 60 percent on average of covered health care expenses (e.g. coverage offered does not have at least a 60-percent actuarial value).
After 2014, penalty amounts are indexed by a premium adjustment percentage for the calendar year.
The Congressional Budget Office expects the penalties to generate $52 billion toward the overall cost of health reform by 2019. The Department of Health and Human Services estimates that fewer than 2 percent of large American employers will have to pay the assessments.
Disclaimer: This blog is not intended to represent legal advise and one should consult with a tax and/or legal expert.



